Did you know? By 2025, the natural language generation market is expected to surpass $1 billion, showcasing its integration across all digital sectors
Unveiling Natural Language Generation: The Startling Growth of Language Processing
"By 2025, the natural language generation market is expected to surpass $1 billion, showcasing its integration across all digital sectors."
- Adoption of natural language generation tools in business analytics and reporting has cut manual labor by up to 60% in some organizations.
- Customer service chatbots powered by natural language generation are now handling millions of queries per day with high accuracy.
- NLG systems are now integrated into smart home devices and voice assistants, generating responses in real time.
- The accessibility of natural language tools is democratizing content creation for smaller businesses and educators.

What You'll Learn About Natural Language Generation
- The definition and evolution of natural language generation
- How language generation fits into the broader field of natural language processing
- Core concepts, mechanisms, and leading NLG systems
- Real-world applications and industry impacts
- Key differences: NLG vs NLP, Generative AI, and LLMs
- Critical challenges and ethical considerations
- Emerging trends: machine learning, neural networks, and language models
Understanding Natural Language Generation: Definition and Fundamentals
What is Natural Language Generation?
Natural language generation (NLG) is a discipline within artificial intelligence and natural language processing that focuses on transforming data into coherent, human-language text. It forms the backbone of many systems you encounter every day, from smart chatbots to automatic news writers. Unlike simple templates, NLG systems use advanced algorithms and, increasingly, neural networks to generate dynamic, contextually accurate responses or summaries. The process often begins by analyzing large amounts of raw or structured data, determining what information is valuable, and outputting it as sentences or paragraphs that read naturally—mirroring human communication.
These innovations allow businesses to automate data analysis and reporting, enabling more time for strategic thinking and less for repetitive writing. Modern NLG systems have evolved from simple rule-based approaches to sophisticated tools capable of generating product descriptions, personalized emails, and customer reports. By leveraging a language model and deep learning, NLG can adapt tone, context, and complexity according to user needs, bridging the gap between raw information and meaningful, actionable insights.
The Origins and Evolution of Language Generation
The roots of language generation can be traced back to early computational linguistics and computer science. Early NLG systems operated on scripted rules, where every possible sentence or phrase had to be manually programmed. With steady advances, especially the advent of machine learning and neural network approaches, systems began to "learn" from real examples rather than rely solely on hard-coded logic. Over the last decade, transformative breakthroughs in deep learning have enabled today's NLG platforms to mimic tone, context, and even the nuances of humor or cultural references.
Recent years have seen the integration of large language models (LLMs), which train on extensive text datasets to generate impressive, contextually-aware output. These technological leaps have shifted NLG from niche research to mainstream business, allowing industries from finance to healthcare to automate reporting, customer communication, and content generation at scale.
The Relationship Between Natural Language Generation and Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is the overall field focused on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and interact using the complexities of human language. Within this umbrella, natural language generation is the component that specializes in generating and authoring human-like text outputs. While NLP includes text analysis, translation, speech recognition, and more, NLG focuses on the generation system aspect—producing new text rather than merely understanding it.
This distinction is critical because the underlying processes, models, and challenges for comprehension versus generation diverge. NLG systems require advanced strategies not only to ensure grammatical correctness but also context, accuracy, and engagement. Advances in NLP—from attention mechanisms to context-aware models—have fueled the sophistication and reliability of NLG outputs, integrating deeper levels of language understanding into the creative act of writing itself.

How Natural Language Generation Works: From Data to Text
The Five Core Stages of Natural Language Generation
- Analyzing data
- Content determination
- Sentence planning
- Linguistic realization
- Text aggregation
The NLG process is a sophisticated workflow that involves several distinct stages designed to transform structured data into natural, readable text. First, data analysis identifies which facts, trends, or relationships from the input data are significant. Next, content determination decides what information should be included based on the intended audience or document plan. Once these core details are established, sentence planning organizes information logically, ensuring clarity and flow.
The linguistic realization phase translates this organization into grammatically correct sentences, utilizing language rules and stylistic preferences. Finally, text aggregation brings everything together, presenting the generated text in unified paragraphs or sections. This multi-layered approach separates modern NLG from mere data spitting—it crafts meaningful, contextualized narratives optimized for human readers and applications.
| Aspect | Traditional NLG Systems | Neural Network-Based NLG |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Rule-based, template-driven | Deep learning, attention mechanisms |
| Flexibility | Limited customization and expressiveness | Dynamic, context-aware generation |
| Learning Source | Manual script and input | Large datasets, automated learning |
| Output | Repetitive, formulaic text | Human-like, diverse, adaptive output |
| Application | Simple reporting, fixed responses | Creative tasks, conversation, contextual summaries |
Key Components of Language Generation Systems
NLG Systems: Architecture and Frameworks
The backbone of any successful nlg system is its architecture—a modular design that enables the flexible conversion of data to text. A modern NLG system typically comprises multiple layers: a data input/analysis layer, a content planning engine (sometimes called a document planner), a sentence planner, and realization modules for rendering output text. Standard frameworks like SimpleNLG and NaturalOWL offer extensible platforms, but enterprise solutions often leverage proprietary architectures enhanced with machine learning for adaptability and up-to-date language use.
This layered structure means developers can tailor the generation system to domain-specific needs, whether for financial reports, weather summaries, or personalized marketing emails. Rigorous testing, scalable frameworks, and sophisticated feedback loops are critical elements, ensuring high fidelity, relevance, and user-specific customization of the generated text.
Machine Learning in Natural Language Generation
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Deep Learning methods
Machine learning and, specifically, deep learning have dramatically advanced how NLG systems learn from data and improve over time. Supervised learning methods feed labeled training data (examples of inputs and correct outputs) into language models, allowing systems to replicate and expand on human writing patterns. In contrast, unsupervised learning explores unlabeled datasets, uncovering structures and correlations independently—a technique critical in adapting to new vocabularies and writing styles.
Deep learning, especially via neural networks, introduces capabilities like the attention mechanism, which allows NLG platforms to consider context over extended passages of text. This results in responses that are not only accurate but nuanced and variable—necessary for everything from product descriptions to customer chatbots. As models continue to train on broader and more diverse datasets, the results become increasingly sophisticated, reducing bias and improving relevance across different industries and applications.
The Role of Language Models and Neural Networks
Today's breakthroughs in language generation are largely credited to advanced language models powered by neural networks. These systems—ranging from transformer models like GPT-style architectures to recurrent neural networks—learn complex patterns and relationships within language at scale. With millions (or even billions) of parameters, these models understand nuance, adapt tone, and generate fluid, context-aware text.
The synergy between neural networks and language models allows NLG systems to go beyond basic sentence formation. Instead, they generate text that is both semantically accurate and contextually relevant, offering significant improvements in applications such as conversational AI, summarization tools, and creative writing assistants. The success of these NLG applications hinges on their ability to represent and reproduce the intricacies of natural human communication.

Applications of Natural Language Generation in the Real World
Data Analysis and Reporting
One of the most transformative uses for natural language generation is automating data analysis and report writing. Businesses use NLG to convert structured data such as sales figures, financial metrics, and performance indicators into clear, digestible reports in seconds. This not only streamlines operations but also ensures accurate, bias-free narratives that can be tailored to individual stakeholders or clients.
Automated report generation reduces manual effort, minimizes human error, and enables organizations to distribute up-to-date insights faster than ever. Whether it’s daily dashboards for executives or detailed compliance summaries for accounting, NLG empowers teams to make better decisions based on fast, reliable information.
Text Generation and Conversational AI
Text generation lies at the heart of modern conversational AI systems, including voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant. Powered by NLG, these platforms generate responses to queries, hold flowing conversations, and even execute commands with human-like fluency. NLG-driven chatbots are used extensively for customer service, handling millions of inquiries per day with responsive, context-aware language.
As these AI assistants become more sophisticated, they integrate seamlessly with daily routines—from scheduling meetings to setting reminders and ordering groceries. This marks a leap in human language interaction with technology, making intelligent communication possible at scale.
Natural Language Generation in Content Creation
Content creation has been revolutionized by NLG, enabling everything from news article writing to automated product descriptions for e-commerce. Journalists and marketers use NLG software to draft reports, blogs, and marketing materials at speed—freeing up time for more creative or strategic tasks. Academic and technical writers leverage NLG for summarizing research findings or generating repetitive documentation.
The adaptability of NLG means content can be customized by tone, complexity, audience, or even cultural references, ensuring both consistency and variety. This translates into scalable, high-quality output tailored precisely to audience needs across industries.
Business Process Automation and Customer Experience
Businesses are turning to NLG to automate routine processes—such as onboarding emails, invoice explanations, or customer support responses. This not only saves time but enhances customer experience by providing rapid, relevant, and accurate communication. Advanced NLG solutions allow for hyper-personalization: automatically generating unique responses based on past interactions, preferences, or transaction history.
As a result, organizations can scale up services without sacrificing quality or introducing delays, enabling a new level of competitiveness and agility in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.

NLG vs NLP: Clarifying the Distinction
"NLP is the umbrella field, but natural language generation is the art and science of letting machines author human-like text." -- AI Researcher
- NLP (natural language processing) covers analyzing, interpreting, and understanding human language—including tasks like language translation and sentiment analysis.
- NLG (natural language generation) specifically focuses on systems that generate text—such as report generation, automatic email writing, or AI chatbots.
- Some use-cases, like dynamic content writing or personalized recommendations, are unique to NLG systems and not typically handled by pure NLP solutions.
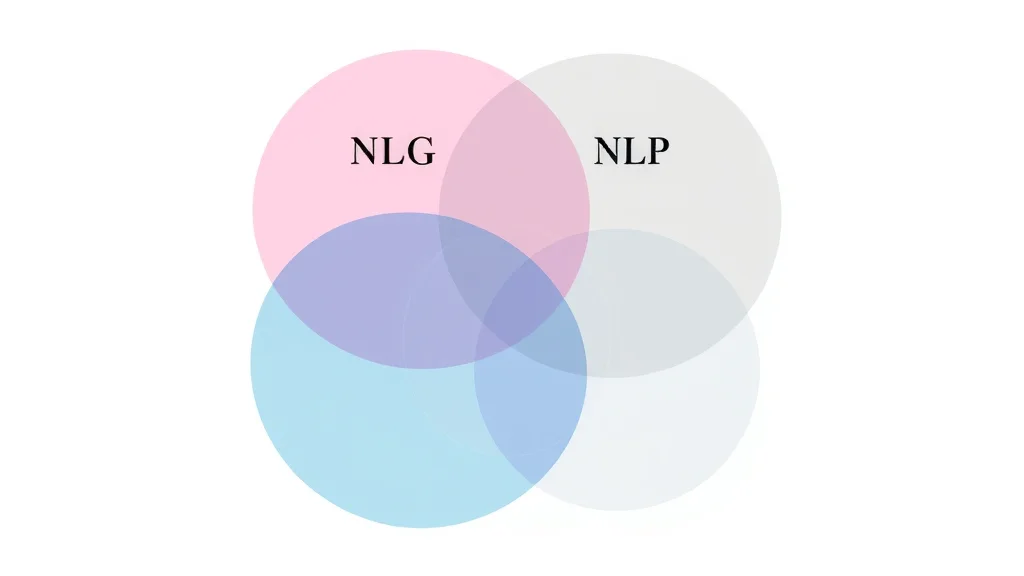
Natural Language Generation vs Generative AI vs LLMs
Defining Generative AI and Large Language Models
Generative AI encompasses a wider class of AI systems able to produce new content, from images and music to speech and text. Natural language generation is one application area, focusing specifically on text. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI's GPT or Google's PaLM, are advanced neural architectures trained on vast text corpora to understand and generate human-like language. These models drive much of today’s NLG through their ability to handle nuance, context, and diverse languages.
While generative AI creates in multiple media types, LLMs are optimized for language generation—powering chatbots, writers, and assistants with contextually appropriate, semantically rich output.
Comparing Features and Use-Cases
The key differences rest in specialization and application. NLG systems are task-specific—generating clinical reports, sports narratives, or marketing emails. Generative AI can include NLG, but also covers audio, video, and multimodal outputs. LLMs provide a foundational layer, unlocking broad capabilities for any NLG or NLP use-case. Choosing among these solutions hinges on project scope, required adaptability, and the types of data or interaction involved.
| Feature | Natural Language Generation (NLG) | Generative AI | Large Language Models (LLMs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Text generation from structured/unstructured data | Multimodal content creation (text, image, audio, etc.) | AI frameworks trained for language tasks |
| Core technology | Rule-based, template systems, neural networks | Deep learning, generative adversarial networks | Transformers, neural networks, attention mechanisms |
| Main use-cases | Reports, chatbots, summaries, emails | Image synthesis, voice cloning, text-to-image | Translation, summarization, dialog, text creation |
| Flexibility | High for language; limited beyond text | Very high, all content types | Extremely high for language tasks |
| Popular examples | Arria NLG, Automated Insights | DALL·E, Jukebox | GPT-3, BERT, T5 |

Leading Natural Language Generation Systems
Overview of State-of-the-Art NLG Systems
The top nlg systems on the market today, including industry leaders like Arria, Automated Insights, AX Semantics, and Narrative Science, all leverage a combination of rule-based techniques and neural network advancements. These platforms provide user-friendly interfaces, API integration, and support for a range of languages and verticals, from finance to e-commerce.
State-of-the-art NLG software can generate everything from weekly financial summaries to real-time sports updates, adapting language style and technicality based on audience or communication channel. The flexibility and scalability of these systems have led to widespread adoption across sectors around the world.
How Modern NLG Systems Leverage Artificial Intelligence
AI-driven NLG solutions rely on robust machine learning and language models to produce more nuanced, accurate, and relevant text. These platforms collect user feedback, refine document plans automatically, and adapt to ever-changing data flows. Recent advancements in deep learning allow users to fine-tune tone, sentiment, and subject-matter precision—enabling high-quality, domain-specific output with minimal manual intervention.
This fusion of artificial intelligence and language technologies represents a turning point in automation and human-computer interaction, making it possible for organizations of all sizes to deliver enriched, natural, and highly engaging communication.

Challenges and Considerations in Language Generation
Accuracy and Bias in Natural Language Generation
As with any AI-driven technology, ensuring the accuracy of generated text is a constant challenge. While NLG systems have advanced greatly, they may still misinterpret or distort complex or ambiguous data, resulting in factual errors or misleading summaries. Equally important is the issue of bias: because language models learn from large, often unfiltered datasets, they can inadvertently replicate or exacerbate societal, cultural, or gender biases present in the original data.
Continuous monitoring, fine-tuning, and diversified training data are vital measures for promoting both accuracy and fairness in automated language generation. Developers and organizations must stay vigilant, proactively identifying and correcting issues as they arise to maintain trust and credibility in NLG applications.
Ethics and Responsible Use
With great power comes responsibility. The proliferation of NLG amplifies concerns about misinformation, content misuse, and “deepfake” text creation. It's essential for businesses and developers to implement transparent usage policies, obtain consent when using personal data, and establish clear accountability for NLG outputs.
Responsible NLG design involves safeguards such as bias detection, output validation, and user education about AI-generated content. As the role of NLG in public discourse increases, so too does the importance of an ethical framework guiding its deployment and evolution.
Limitations of Current NLG Systems
Despite their remarkable progress, current NLG systems still face significant limitations. Context loss in long documents, difficulty in handling ambiguous language, inability to inject true creativity, and the need for large computational resources all restrict their utility. Moreover, high-quality nlg software may come with substantial licensing costs, complex implementation steps, and maintenance burdens.
Solving these challenges requires ongoing research in machine learning, neural networks, and computational linguistics, alongside practical, real-world testing and user feedback. Only by addressing these issues can NLG fulfill its full promise as a universal communication tool.

Emerging Trends in Natural Language Generation Technology
Recent Breakthroughs in Neural Networks and Language Models
Recent years have ushered in revolutionary advancements in both neural networks and language models. The introduction of transformer architectures and models like BERT, GPT-3, and T5 has made it possible to generate longer, more coherent, and contextually relevant text automatically. These breakthroughs also enable real-time translation, contextual summarization, and creative storytelling at scales previously unattainable.
By leveraging increased computational power and ever-larger datasets, NLG systems have improved in fluency, contextual awareness, and the ability to mimic specific writing styles. These developments are setting new standards for the kind of experiences users expect in digital communication and automation tools.
Future Directions: Multimodal NLG and Cross-Language Generation
Looking ahead, the next frontier for NLG involves multimodal systems capable of combining text, images, and even voice to create more engaging, interactive experiences. Cross-language NLG is also poised for major growth—empowering machines to seamlessly generate content in multiple languages, regions, or dialects, breaking down communication barriers worldwide.
As AI research continues to push boundaries, the convergence of modalities, real-time adaptation, and interoperability are likely to define the future of how information is authored, shared, and consumed in the global digital economy.
People Also Ask: Answers to Common Queries About Natural Language Generation
What is a natural language generation?
Answer: Natural language generation is a subfield of artificial intelligence and natural language processing that automatically converts structured data into human-like natural language text.
What is the difference between NLG and NLP?
Answer: NLP encompasses understanding, analyzing, and processing human language, while NLG specifically refers to generating meaningful language output, typically in the form of text.
What are the 5 stages of NLP?
Answer: The five typical stages of NLP are Lexical Analysis, Syntactic Analysis, Semantic Analysis, Discourse Integration, and Pragmatic Analysis.
What is NLP vs Generative AI vs LLM?
Answer: NLP refers to natural language processing, which deals with computer-human language interactions. Generative AI refers to algorithms that can create new content. LLMs (Large Language Models) are AI models trained to understand and generate large volumes of human language.
Best Practices and Checklist for Implementing Natural Language Generation
- Define clear objectives for language generation use
- Choose the appropriate NLG system or platform
- Ensure access to high-quality training data
- Continuously monitor outputs for accuracy and bias
- Regularly update and retrain models as needed
FAQs: Natural Language Generation Essentials
-
How does a neural network improve text generation?
Neural networks identify complex patterns and context in language, enabling NLG systems to generate more coherent, natural, and relevant text output than traditional rule-based systems. -
What industries benefit most from advanced natural language generation?
Sectors like finance, healthcare, e-commerce, journalism, and customer service gain major efficiencies from NLG through automation and rapid, accurate communication. -
Can language models understand context in conversation?
Advanced language models use attention mechanisms and vast training data to remember context across multiple dialogue turns, improving relevance and naturalness in AI conversations. -
What are common pitfalls in deploying NLG systems?
Pitfalls include data bias, factual errors in output, regulatory and ethical challenges, and over-reliance on automation without adequate human oversight. -
How does data analysis enhance language generation?
Robust data analysis ensures that only the most relevant information is selected for generation, improving accuracy, clarity, and value in automated reports and narratives.
Key Takeaways: The Transformative Impact of Natural Language Generation
- Natural language generation is a catalyst for human-like machine communication
- Modern NLG systems integrate advanced language models and neural networks
- Ethical deployment and accuracy are central challenges
- The adoption and future of NLG promise broad societal and business benefits
Final Thoughts: Where Natural Language Generation Is Heading
"The pace of progress in natural language generation will fundamentally change how we interact with technology."
Explore Leading Natural Language Generation Tools Today
- Experiment with top-rated NLG platforms in your projects
- Request a free trial and see the difference natural language generation can make
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment